VMR-FR3300L
The development of mobile robots has been a rapid progression from "low-end" to "intelligent," and from "weak perception" to "strong perception."
Machine Vision Holds Great Potential
With advancements in LiDAR technology, laser navigation has become one of the mainstream methods in the industry. AMR solutions based on laser SLAM navigation have been implemented in various applications. However, as laser navigation becomes more widely used, its limitations are also being exposed, particularly in terms of stable positioning in complex environments.
In dynamic environments where the position of goods is constantly changing and fixed reference points are rare, robots using laser SLAM often struggle with reliable positioning. Frequent movements in and out of storage areas mean the environment continually changes, making consistent and accurate positioning difficult.
In large, open workshops, where the distance between steel columns is wide, LiDAR-equipped robots face issues due to sparse point clouds and a lack of reliable reference points, reducing the reliability of their navigation.
Visual SLAM, however, uses depth cameras on the robot to capture images of the surrounding environment and generate dense point clouds. This rich environmental data allows robots to maintain stable positioning even in the face of local changes, offering superior adaptability to various scenes.
The Challenging Path of Vision-Based Solutions
Despite the clear advantages of visual SLAM in terms of environmental adaptability, few companies in the market are adopting it. The primary reason is the high technical barrier of depth vision, which many AMR companies cannot develop in-house due to the lack of a visual research and development team and relevant technological expertise.
LANXIN’s MRDVS division, though a young team, has nearly 20 years of experience in optics and computer vision. This expertise has enabled them to build a comprehensive R&D capability combining computer vision and mobile robotics.
Compared to the more mature LiDAR technology, depth vision is a "challenging path" — one that MRDVS has chosen to pursue. After years of technical development, MRDVS has established a robust and complete deep vision system for mobile robots, including self-developed 3D vision sensors and perception algorithms. LANXIN is now the first company in China to offer a fully integrated 3D vision hardware and software solution for mobile robots.
This system enables robots to perform visual localization, obstacle avoidance, and high-precision docking, significantly improving safety, stability, and intelligence, while meeting the needs of more complex environments.
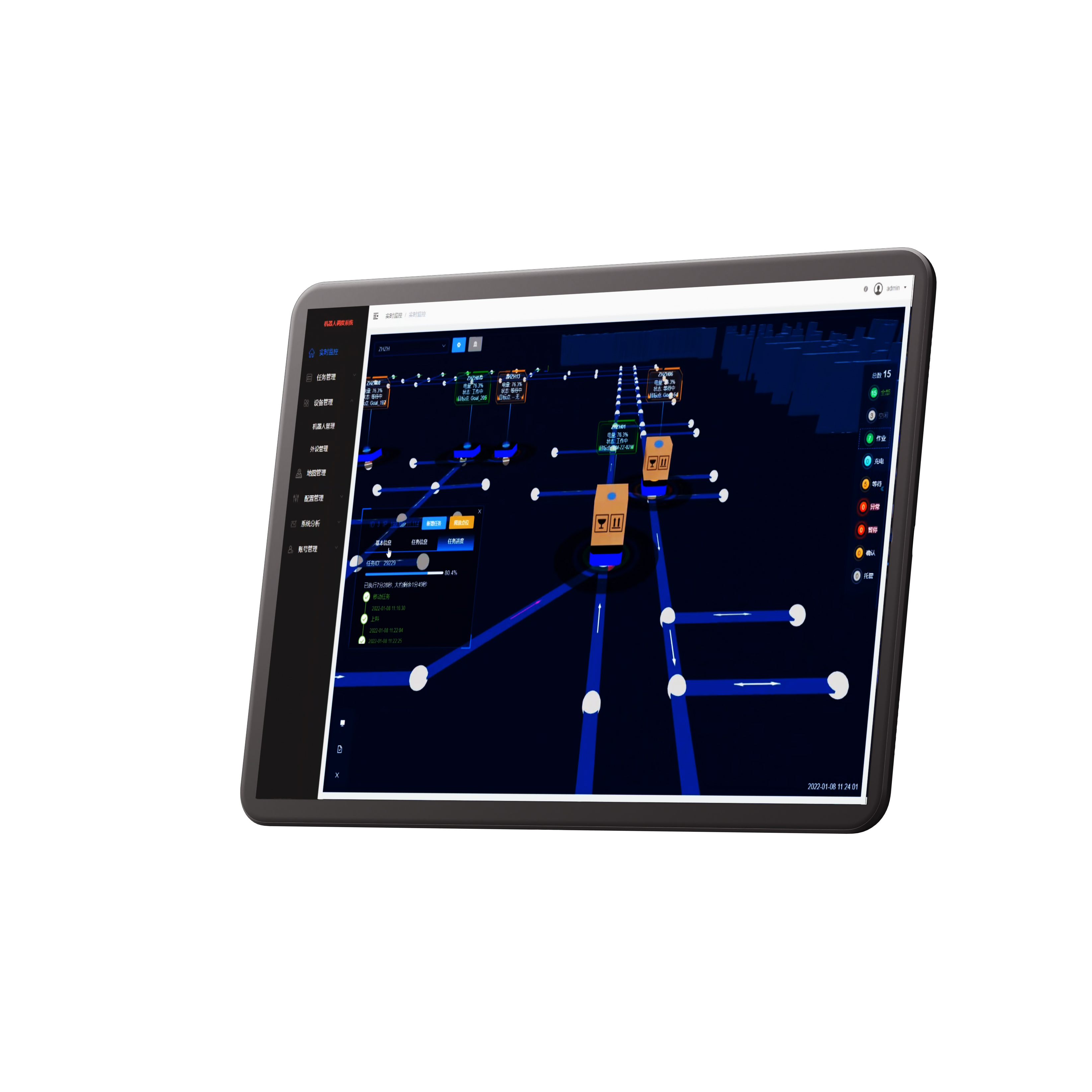
Case Study: Large-Scale Warehouse Solution
Take, for example, a large contract manufacturer’s warehouse with over 3000 storage positions. Goods frequently enter and exit, and the arrangement of pallets and items is constantly changing, without fixed reference points. The robot may also encounter workers or obstacles like cartons left in the aisles. Additionally, to maintain the warehouse's aesthetic and ease of deployment, the client preferred not to use floor-marked QR codes.

In this scenario, the available options were limited to either laser SLAM or vision SLAM-equipped forklifts. However, robots using laser SLAM face significant challenges in reliably locating themselves in such dynamic environments. The client ultimately chose LANXIN’s vision SLAM solution.
MRDVS provides LANXIN's forklifts with an integrated solution for visual positioning, pallet docking, and obstacle avoidance.
For navigation, the forklift uses a 3D vision SLAM system. Depth cameras capture unmarked 3D environment data to generate dense point clouds and link the collected data with the robot’s actual position to achieve autonomous localization and navigation. The advantages include:
Reliability and stability, unaffected by people, vehicles, or logistics.
Adaptability to dynamic environments, with changes in layout or pallet positions having no impact.
High precision, with an accuracy of +/-1cm in typical environments.
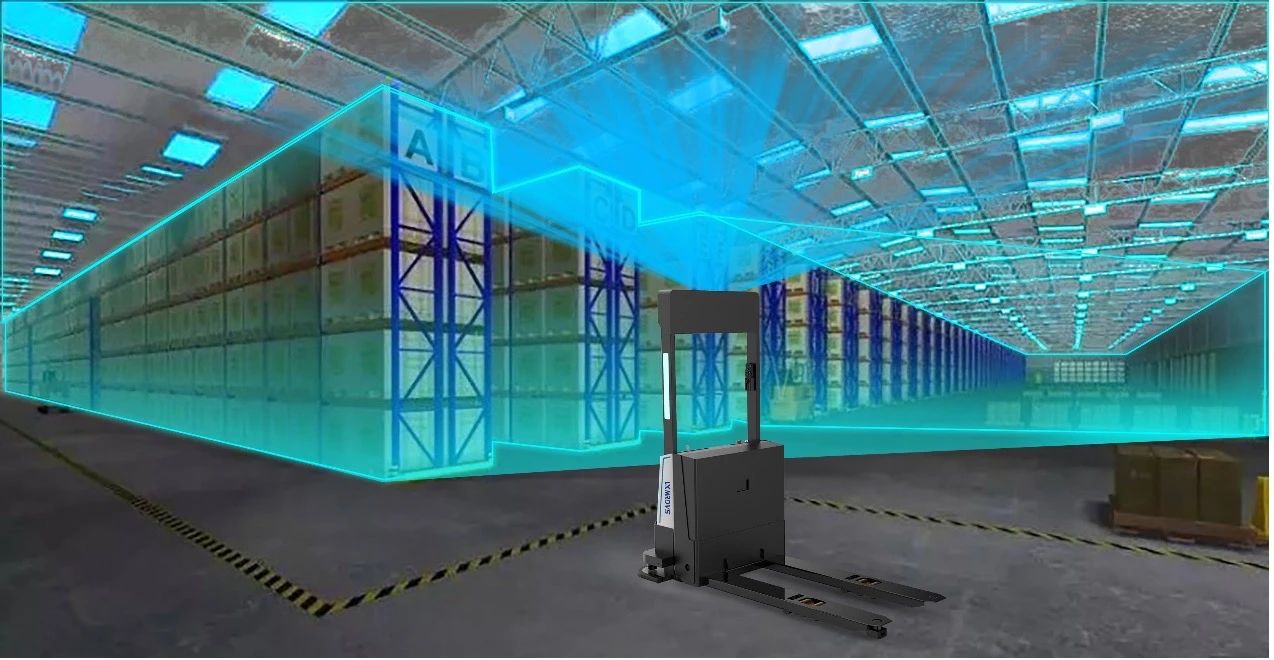

For pallet docking, the forklift uses a 3D vision docking system. A custom-designed camera captures images to generate a point cloud of the pallet, and combined with LANXIN’s vision algorithms, the robot can calculate misalignment values and adjust its pose and fork direction to successfully pick up the pallet.
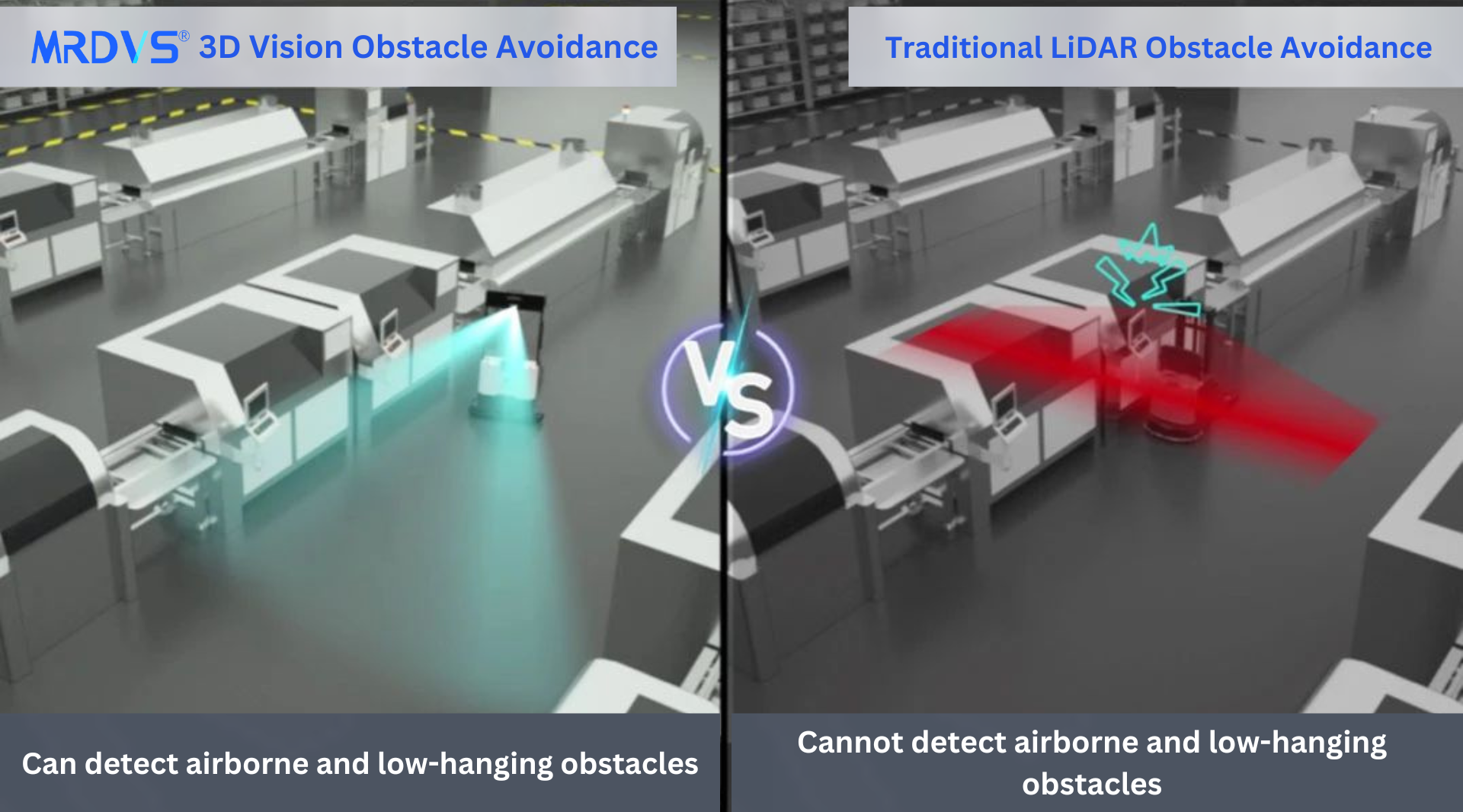
Additionally, the forklift is equipped with a 3D vision-based obstacle avoidance system, which detects airborne and low-hanging obstacles within the robot’s field of view, ensuring safe operation.
With MRDVS’s deep vision system, LANXIN has delivered a smart, unmanned warehouse logistics solution that fully meets the client's requirements.
Visit LANXIN Robotics: LANXIN Robotics | Empower Robots with the Intelligence to See and Serve the Human
Visit MRDVS Technology: 3D Robot Camera | Empowering Robots to Comprehend the World
Contact Us
Lanxin Technology, 7-802,
China Artificial Intelligence Town,
No.1818-2 Wenyi West Road,
Hangzhou, Zhejiang, China
marketing@lanxincn.com
Popular Products
Cases
Industry


















